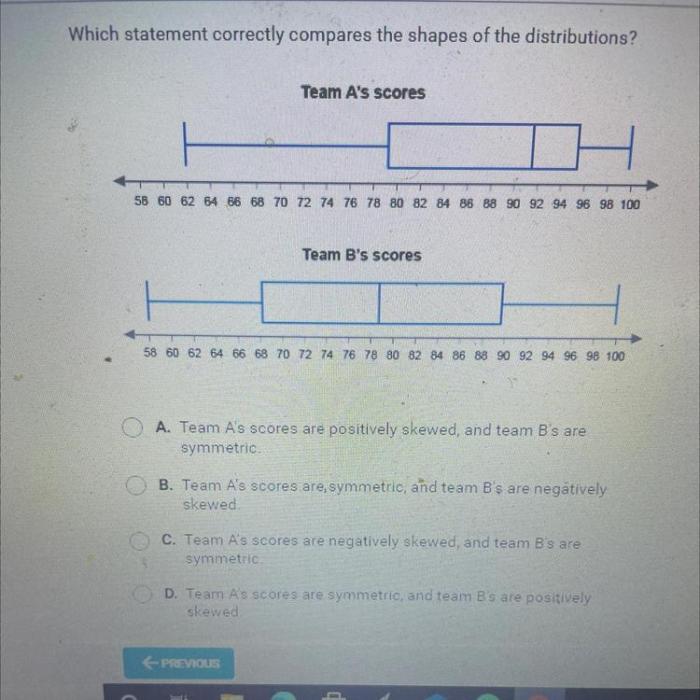
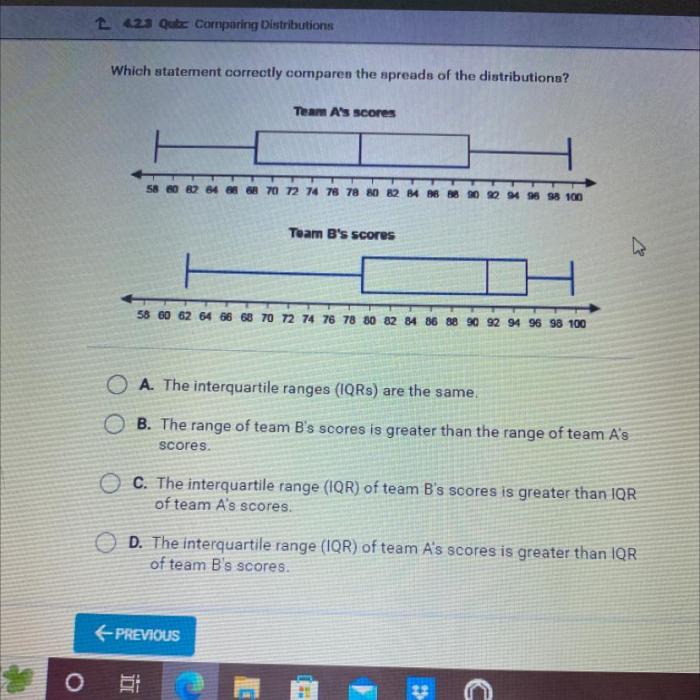
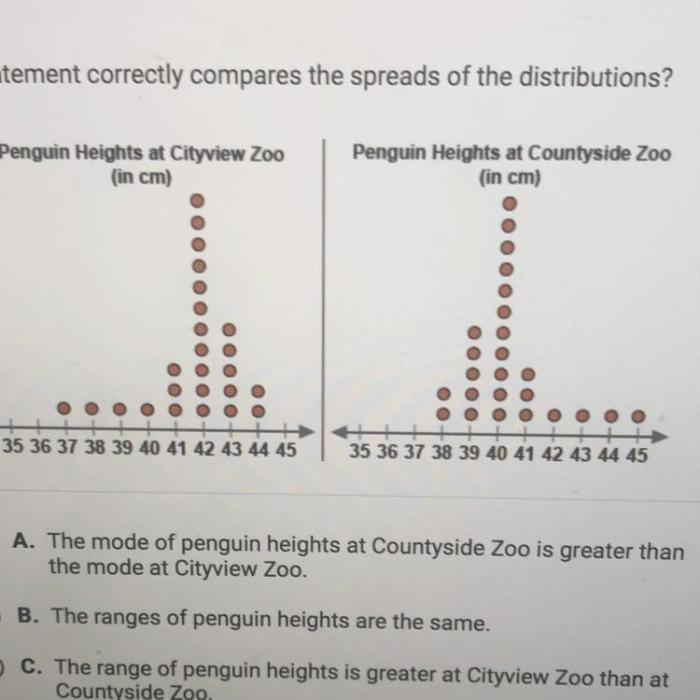
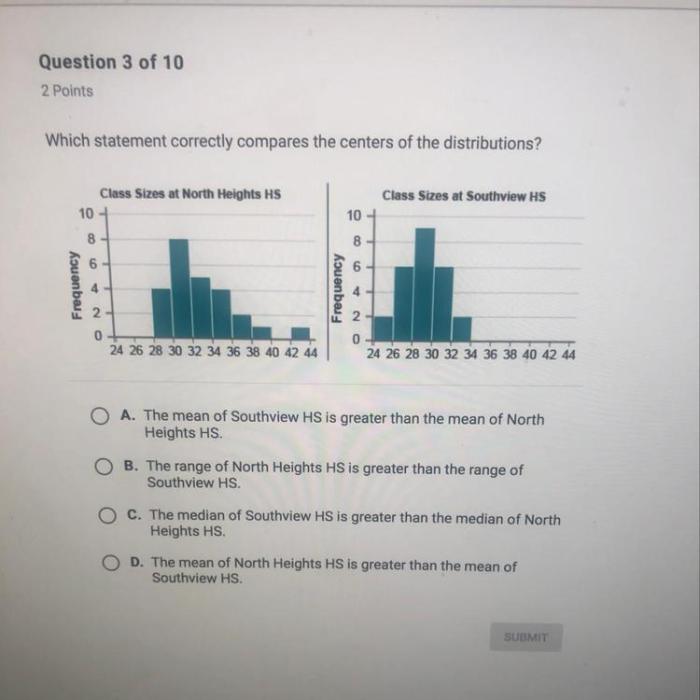
Which statement correctly compares the spreads of the distributions – Embarking on an exploration of which statement correctly compares the spreads of distributions, this discourse delves into the intricacies of data analysis, providing a comprehensive examination of the topic. By unraveling the fundamental concepts, methodologies, and applications, this analysis aims to illuminate the nuances of comparing distribution spreads, empowering readers with a deeper understanding of statistical inference.
This discourse will elucidate the significance of distribution spread comparison, demonstrating its utility in diverse scenarios. Furthermore, it will explore the statistical techniques employed for this purpose, including hypothesis testing and the interpretation of results. Through a rigorous examination of these concepts, this analysis seeks to provide a thorough understanding of which statement correctly compares the spreads of distributions.
1. Data Distribution Analysis
Data distribution mengacu pada cara data tersebar di sekitar nilai rata-rata. Memahaminya sangat penting untuk menganalisis dan menafsirkan data secara efektif. Jenis distribusi data yang umum meliputi distribusi normal, binomial, dan Poisson.
Ukuran yang digunakan untuk menggambarkan penyebaran distribusi meliputi jangkauan, varians, dan standar deviasi. Jangkauan adalah selisih antara nilai tertinggi dan terendah dalam dataset, sementara varians dan standar deviasi mengukur seberapa jauh nilai data tersebar dari nilai rata-rata.
2. Comparing Distribution Spreads
Membandingkan penyebaran distribusi berguna untuk menentukan apakah dua populasi atau lebih memiliki variabilitas yang sama. Ini dapat dilakukan melalui uji F atau uji Levene.
Uji F digunakan untuk membandingkan varians dari dua populasi yang berdistribusi normal. Uji Levene adalah uji non-parametrik yang digunakan untuk membandingkan varians dari dua populasi yang mungkin tidak berdistribusi normal.
3. Hypothesis Testing for Distribution Spreads, Which statement correctly compares the spreads of the distributions
Pengujian hipotesis memainkan peran penting dalam membandingkan penyebaran distribusi. Hipotesis nol biasanya menyatakan bahwa tidak ada perbedaan dalam penyebaran antara dua populasi, sementara hipotesis alternatif menyatakan bahwa ada perbedaan.
Langkah-langkah dalam melakukan uji hipotesis untuk penyebaran distribusi meliputi menetapkan hipotesis, memilih uji statistik yang sesuai, menentukan tingkat signifikansi, menghitung nilai uji statistik, dan mengambil keputusan.
4. Interpreting Results
Hasil uji hipotesis dapat ditafsirkan dengan melihat nilai p. Nilai p yang kecil (biasanya kurang dari 0,05) menunjukkan bahwa ada perbedaan yang signifikan dalam penyebaran antara dua populasi. Dalam hal ini, hipotesis nol ditolak dan hipotesis alternatif diterima.
Nilai p yang besar menunjukkan bahwa tidak ada perbedaan yang signifikan dalam penyebaran antara dua populasi. Dalam hal ini, hipotesis nol dipertahankan dan hipotesis alternatif ditolak.
FAQ Overview: Which Statement Correctly Compares The Spreads Of The Distributions
What is the purpose of comparing distribution spreads?
Comparing distribution spreads allows researchers to assess the variability or dispersion of data within different distributions. This helps in understanding the consistency and predictability of the data, as well as identifying any significant differences between the distributions.
What are the common methods used to compare distribution spreads?
Common methods for comparing distribution spreads include the F-test, Levene’s test, and Bartlett’s test. These tests evaluate the equality of variances between two or more distributions, providing insights into the homogeneity of the data.
How do you interpret the results of a hypothesis test for distribution spreads?
The results of a hypothesis test for distribution spreads are typically presented in terms of a p-value. A low p-value (typically less than 0.05) indicates that there is a statistically significant difference in the spreads of the distributions, while a high p-value suggests that there is no significant difference.