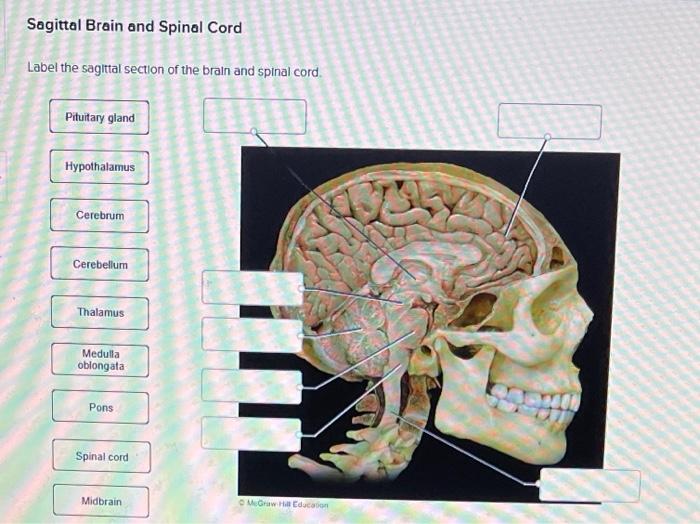
Label the sagittal section of the brain and spinal cord. – Label the sagittal section of the brain and spinal cord, a procedure of paramount importance in neuroanatomy, offers an intricate glimpse into the structural organization of the central nervous system. This detailed examination unveils the intricate arrangement of neural components, providing invaluable insights into their functions and clinical significance.
Delving into the intricacies of sagittal sections, we embark on a journey to identify and understand the major structures of the brain and spinal cord, unraveling their complex interconnections and functional roles. Moreover, we explore the clinical applications of sagittal sections, highlighting their utility in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions.
Overview of Sagittal Section of the Brain and Spinal Cord
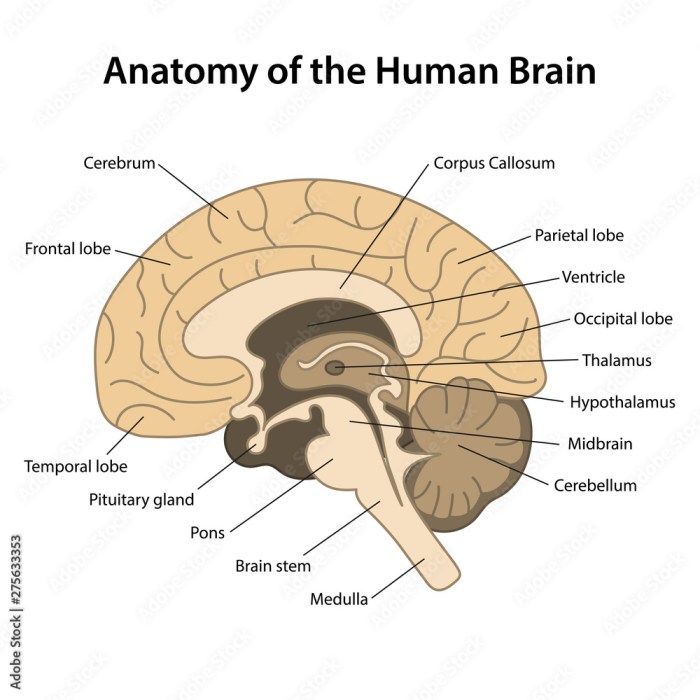
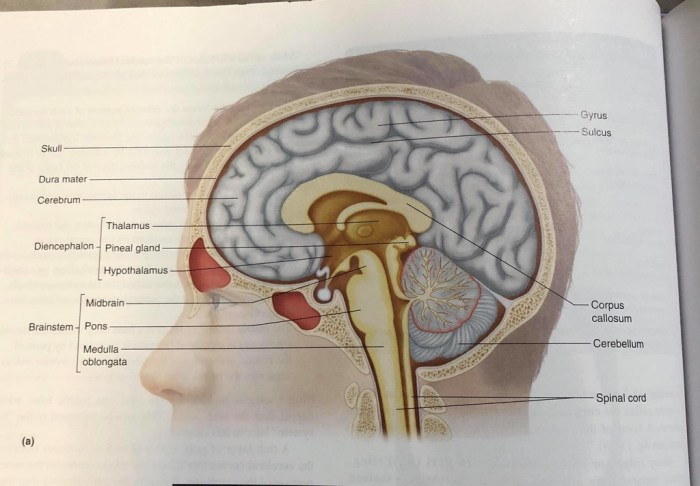
A sagittal section is a vertical cut through the brain and spinal cord that divides them into left and right halves. It provides a comprehensive view of the central nervous system’s midline structures.
The sagittal section reveals various structures, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, ventricles, spinal cord, gray matter, white matter, and spinal canal.
Structures of the Sagittal Section of the Brain
The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, appears in the upper portion of the sagittal section. It is responsible for higher-level functions such as cognition, perception, and voluntary movement.
Below the cerebrum lies the cerebellum, which plays a crucial role in coordination, balance, and motor control.
The brainstem, located at the base of the brain, connects the brain to the spinal cord. It controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and sleep-wake cycles.
Within the brain, ventricles are fluid-filled cavities that produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
Structures of the Sagittal Section of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord, a long, cylindrical structure, extends from the brainstem down the vertebral column. It transmits sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body.
The sagittal section of the spinal cord reveals the gray matter, which contains nerve cell bodies, and the white matter, which consists of myelinated nerve fibers.
The spinal canal, a central channel within the spinal cord, contains cerebrospinal fluid and protects the delicate nerve tissue.
Clinical Significance of the Sagittal Section, Label the sagittal section of the brain and spinal cord.
Sagittal sections are widely used in medical imaging, particularly in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans.
These sections provide valuable information for diagnosing and treating neurological conditions. They can reveal abnormalities in brain and spinal cord structures, such as tumors, cysts, and herniated discs.
Histological Techniques for Sagittal Sectioning
Histological techniques are employed to prepare sagittal sections of the brain and spinal cord for microscopic examination.
Frozen sectioning involves rapidly freezing the tissue and cutting thin sections. It preserves tissue architecture but can introduce artifacts.
Paraffin embedding entails embedding the tissue in paraffin wax and cutting thin sections. It provides good tissue preservation but requires extensive processing.
Vibratome sectioning uses a vibrating blade to cut thin sections from fresh or fixed tissue. It offers rapid sectioning with minimal tissue damage.
FAQ Compilation: Label The Sagittal Section Of The Brain And Spinal Cord.
What is the sagittal section?
The sagittal section is a plane of section that divides the body or an organ into left and right halves. In the context of the brain and spinal cord, the sagittal section is obtained by cutting along the midline of the body.
What structures are visible in a sagittal section of the brain?
A sagittal section of the brain reveals the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and ventricles.
What structures are visible in a sagittal section of the spinal cord?
A sagittal section of the spinal cord reveals the gray matter, white matter, and spinal canal.
What are the clinical applications of sagittal sections?
Sagittal sections are used in medical imaging to diagnose and treat neurological conditions. They provide valuable information for understanding brain and spinal cord anatomy and pathology.