Unveiling the ‘locating an earthquake epicenter answer key’ unveils a profound understanding of earthquake science, unlocking the secrets behind these formidable natural events. This comprehensive guide delves into the methods, applications, and significance of epicenter location, providing a thorough exploration for seismologists, geologists, and disaster management professionals.
The subsequent paragraphs meticulously describe the principles of triangulation, the role of seismic stations, and the interpretation of arrival time differences. These concepts lay the foundation for determining the epicenter’s distance and ultimately its precise location on a map.
1. Introduction
An earthquake epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the point where an earthquake originates within the Earth. Locating an earthquake epicenter is crucial for understanding the earthquake’s magnitude, assessing potential hazards, and studying earthquake mechanisms.
2. Methods of Locating an Earthquake Epicenter
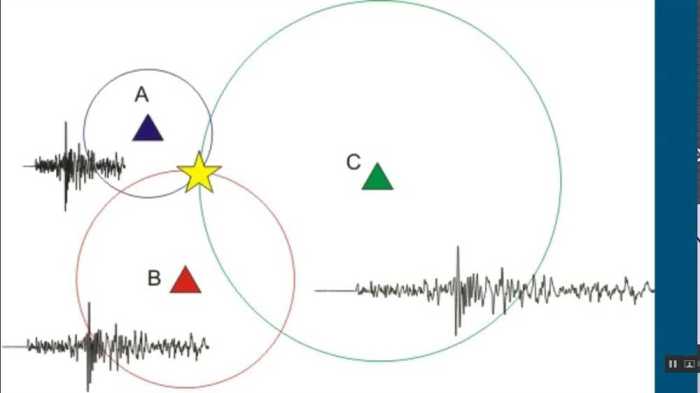
Triangulation Using Seismic Waves
Triangulation is the primary method used to locate an earthquake epicenter. Seismic waves, generated by the earthquake, travel outward from the hypocenter in all directions. Seismic stations, distributed across a region, record the arrival times of these waves.
Role of Seismic Stations and Distribution, Locating an earthquake epicenter answer key
The accuracy of epicenter location depends on the number and distribution of seismic stations. A dense network of stations provides more precise data, while a sparse network can lead to larger uncertainties.
Arrival Time Differences and Wave Velocity
The difference in arrival times of seismic waves at different stations allows us to calculate the distance to the epicenter. This is achieved by multiplying the time difference by the known velocity of the seismic waves.
3. Determining the Epicenter

Calculating Epicenter Distance from Seismic Stations
Using the arrival time differences and wave velocities, we can calculate the distance from each seismic station to the epicenter. These distances are plotted on a map as circles centered at each station.
Drawing Circles and Determining Intersection Point
The intersection point of the circles represents the epicenter of the earthquake. The accuracy of the epicenter location depends on the accuracy of the arrival time data and the distribution of seismic stations.
4. Applications of Epicenter Location: Locating An Earthquake Epicenter Answer Key
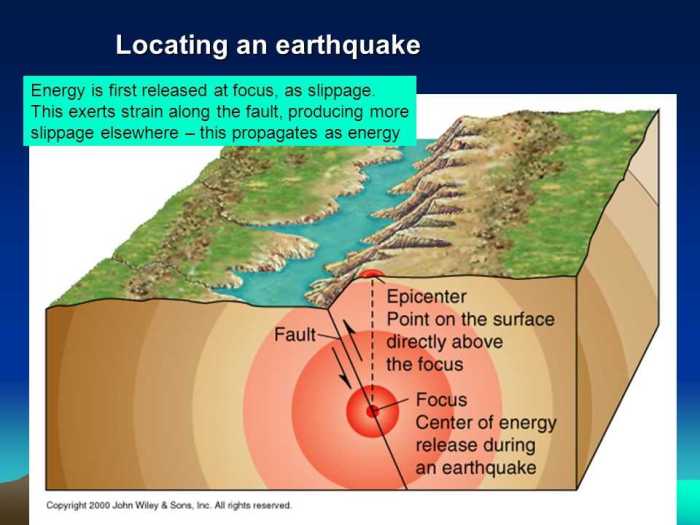
Hazard Assessment
Epicenter location is essential for hazard assessment. By identifying the epicenter, we can estimate the potential impact of the earthquake on nearby communities and infrastructure.
Understanding Earthquake Mechanisms
Epicenter data provides insights into the mechanisms responsible for earthquakes. By analyzing the location and distribution of epicenters, scientists can infer the type of fault that caused the earthquake and the direction of movement.
Seismic Hazard Mapping
Epicenter data is used to create seismic hazard maps, which show the probability of an earthquake occurring in a particular area. These maps help guide building codes and land-use planning decisions.
Quick FAQs
What is an earthquake epicenter?
The earthquake epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the location where the earthquake rupture initiates.
Why is it important to locate an earthquake epicenter?
Locating the epicenter provides crucial information for hazard assessment, understanding earthquake mechanisms, and seismic hazard mapping.
How is an earthquake epicenter located?
The epicenter is determined by analyzing the arrival time differences of seismic waves recorded at multiple seismic stations.