Amoeba sisters video recap dna replication – Introducing the Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: A Comprehensive Guide to DNA Replication, an authoritative exploration into the intricacies of DNA replication, unveiling the fundamental processes that govern the very essence of life. This in-depth analysis delves into the Amoeba Sisters’ captivating video, meticulously dissecting the key concepts and delving into the practical applications of DNA replication in various scientific disciplines.
DNA Replication Overview
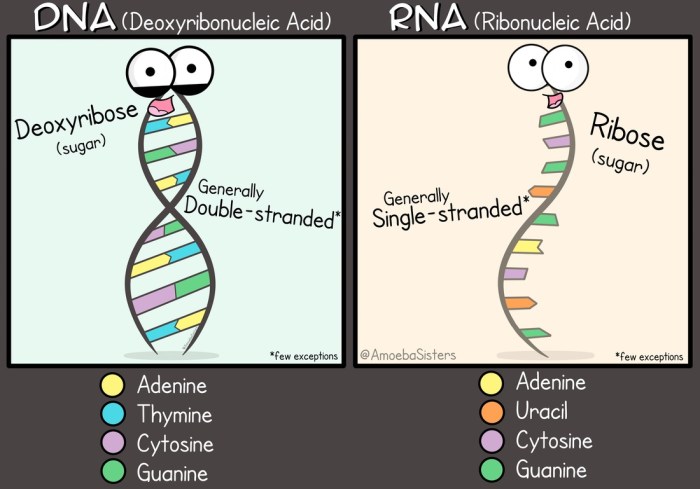
DNA replication is the process by which DNA molecules are copied to produce two identical daughter molecules. This process is essential for cell division, as it ensures that each new cell has a complete copy of the genetic material.DNA replication is carried out by a complex of enzymes, including DNA polymerase, helicase, and ligase.
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, and ligase joins the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap, Amoeba sisters video recap dna replication
The Amoeba Sisters video on DNA replication provides a clear and concise overview of the process. The video covers the basic steps of DNA replication, including initiation, elongation, and termination. It also discusses the role of enzymes in DNA replication and the importance of DNA replication in cell division.One
of the strengths of the video is its use of animation to illustrate the process of DNA replication. This helps to make the process more understandable for students. However, the video does not go into great detail about the mechanisms that ensure the accuracy of DNA replication.
Detailed Analysis of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a complex process that involves a number of steps. The first step is initiation, which occurs when the DNA double helix is unwound and the replication fork is formed. The replication fork is the point at which DNA replication begins.The
second step is elongation, which occurs when DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand. DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3′ end of the DNA strand, so the DNA strand is synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction.The
third step is termination, which occurs when the DNA polymerase reaches the end of the DNA template strand. Once the DNA polymerase has reached the end of the template strand, it releases the newly synthesized DNA strand and the replication fork is disassembled.
Applications of DNA Replication: Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Dna Replication

DNA replication is used in a variety of applications, including biotechnology, genetic engineering, medicine, and forensics. In biotechnology, DNA replication is used to produce recombinant DNA molecules. Recombinant DNA molecules are DNA molecules that contain DNA from two different sources.
Recombinant DNA molecules can be used to produce proteins that are not normally produced by the cell.In genetic engineering, DNA replication is used to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs). GMOs are organisms that have had their DNA altered in a way that does not occur naturally.
GMOs can be used to produce crops that are resistant to pests or diseases, or to produce pharmaceuticals that are more effective or have fewer side effects.In medicine, DNA replication is used to diagnose and treat genetic diseases. Genetic diseases are diseases that are caused by mutations in the DNA.
DNA replication can be used to identify the mutations that cause genetic diseases and to develop treatments for these diseases.In forensics, DNA replication is used to identify individuals. DNA replication can be used to compare the DNA of a suspect to the DNA of a crime scene sample.
If the DNA matches, it can be used to identify the suspect.
FAQs
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication is essential for cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
How do enzymes contribute to DNA replication?
Enzymes such as DNA polymerase and helicase play crucial roles in unwinding the DNA double helix and synthesizing new strands.
What factors can affect the accuracy of DNA replication?
Factors such as DNA damage, mutations, and environmental conditions can impact the accuracy of DNA replication.