Polymers and reactions worksheet answers provide a comprehensive guide to the fascinating world of polymer chemistry. These answers delve into the fundamental concepts of polymers, their diverse reactions, and the techniques used to characterize their properties. By exploring these answers, students and professionals alike can gain a deeper understanding of the materials that shape our modern world.
Polymers, with their unique structures and remarkable properties, play a crucial role in countless industries, from packaging and construction to electronics and medicine. Understanding their behavior and reactivity is essential for developing new and innovative polymer-based materials.
Polymer Basics
Polymers are large molecules composed of repeating structural units called monomers. They possess unique properties such as high strength, flexibility, and electrical insulation, making them essential in various industries.
Examples of common polymers include polyethylene (used in plastic bags), polypropylene (used in containers), and polyvinyl chloride (used in pipes and flooring).
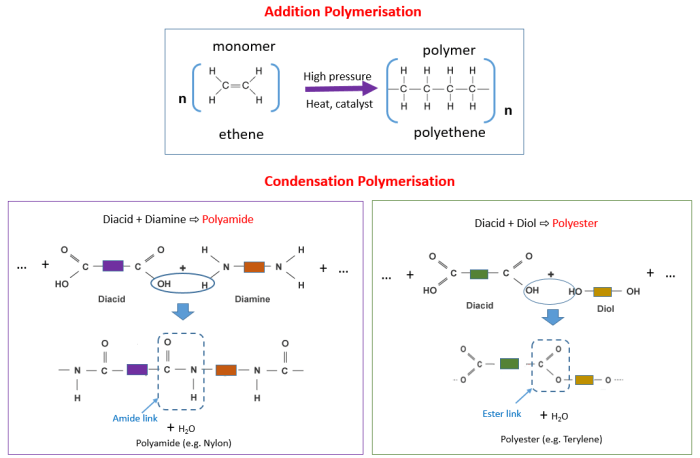
Types of Polymerization Reactions
- Addition polymerization: Monomers with double bonds join together without releasing any byproducts.
- Condensation polymerization: Monomers with functional groups react, releasing small molecules like water or alcohol.
- Cross-linking polymerization: Polymers form additional bonds between their chains, creating a network structure.
Polymer Reactions

Addition Reactions
Addition reactions involve the addition of a small molecule to a polymer chain, typically through a double bond. Examples include the addition of hydrogen or halogens to unsaturated polymers.
Condensation Reactions
Condensation reactions involve the removal of a small molecule (usually water) from two polymer chains, resulting in the formation of a new bond between them. Examples include the formation of polyesters and polyamides.
Cross-Linking Reactions
Cross-linking reactions create covalent bonds between polymer chains, resulting in a more rigid and stronger structure. Examples include the vulcanization of rubber and the curing of epoxy resins.
Factors Affecting Reactivity
The reactivity of polymers in reactions is influenced by factors such as:
- Monomer structure
- Polymer chain length
- Temperature
- Presence of catalysts or inhibitors
Polymer Characterization
Polymer characterization techniques provide valuable information about the structure, properties, and molecular weight of polymers.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopic techniques such as infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy can identify the functional groups and molecular structure of polymers.
Chromatography
Chromatographic techniques such as size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) can determine the molecular weight distribution of polymers.
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis techniques such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) can provide information about the thermal properties and stability of polymers.
Characterization data helps optimize polymer synthesis and processing to achieve desired properties and performance.
Polymer Applications

Polymers have a wide range of applications due to their diverse properties:
Plastics
Polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene are used in the production of various plastic products, including bottles, containers, and packaging materials.
Fibers, Polymers and reactions worksheet answers
Synthetic polymers such as nylon and polyester are used in the manufacturing of clothing, carpets, and other textiles.
Coatings
Polymers like polyurethanes and epoxies are used as coatings for protecting surfaces from corrosion, abrasion, and chemicals.
Adhesives
Polymers such as cyanoacrylates and polyurethanes are used as adhesives for bonding different materials together.
Polymer Sustainability

The production and disposal of polymers pose environmental concerns due to their non-biodegradable nature.
Approaches to improve polymer sustainability include:
- Using renewable resources for polymer synthesis
- Developing biodegradable polymers
- Recycling and reusing polymers
Sustainable polymer products and technologies include bioplastics made from plant-based materials and biodegradable polymers that decompose naturally in the environment.
Helpful Answers: Polymers And Reactions Worksheet Answers
What are the different types of polymerization reactions?
Polymerization reactions can be classified into three main types: addition, condensation, and cross-linking.
How can polymers be characterized?
Polymers can be characterized using various techniques such as spectroscopy, chromatography, and thermal analysis to determine their structure, properties, and molecular weight.
What are the key factors that affect the reactivity of polymers?
The reactivity of polymers is influenced by factors such as their molecular structure, functional groups, and environmental conditions.