Types of hydronic heating systems – Hydronic heating systems, a reliable and efficient means of space heating, have gained prominence in the realm of modern construction. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of hydronic heating, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, and diverse applications. We will delve into the various types of hydronic systems, their components, design considerations, and installation processes, providing a comprehensive understanding of this versatile heating solution.
Overview of Hydronic Heating Systems
Hydronic heating systems are central heating systems that utilize water as the heat transfer medium. They circulate hot water through a network of pipes and tubing, distributing heat throughout a building. These systems offer several advantages, including efficient heat distribution, comfort, and energy savings.
Hydronic heating is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. It is particularly suitable for large spaces where even heat distribution is desired, such as schools, hospitals, and warehouses.
Compared to other heating methods, hydronic systems provide a number of benefits. They offer precise temperature control, resulting in increased comfort and reduced energy consumption. Additionally, hydronic systems are typically more energy-efficient than forced-air systems, as they minimize heat loss through ducts.
However, hydronic systems also have some disadvantages. They can be more expensive to install than other heating systems, and they require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Types of Hydronic Heating Systems

Boiler-Based Systems
Boiler-based hydronic systems utilize a boiler as the heat source. The boiler heats water, which is then circulated through the system’s pipes and tubing. Boiler-based systems are commonly used in large buildings, as they can provide a high heat output.
Heat Pump-Based Systems
Heat pump-based hydronic systems use a heat pump as the heat source. Heat pumps extract heat from the outside air or ground and transfer it to the water circulating in the system. Heat pump-based systems are more energy-efficient than boiler-based systems, but they may not be suitable for all climates.
Solar-Based Systems, Types of hydronic heating systems
Solar-based hydronic systems use solar collectors to heat the water circulating in the system. Solar-based systems are the most energy-efficient type of hydronic heating system, but they require a significant investment in solar panels.
System Components
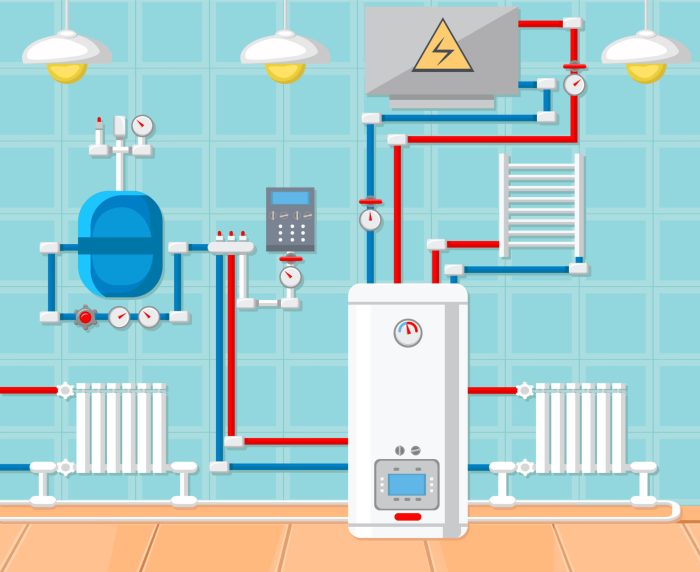
The essential components of a hydronic heating system include:
- Heat source (boiler, heat pump, solar collector)
- Piping and tubing
- Radiators or radiant floor panels
- Control system
The heat source heats the water, which is then circulated through the piping and tubing. The radiators or radiant floor panels release heat into the building, providing warmth and comfort.
The control system regulates the temperature of the water circulating in the system, ensuring that the desired indoor temperature is maintained.
Design Considerations: Types Of Hydronic Heating Systems
When designing a hydronic heating system, several factors must be considered:
- Heat load calculations
- System layout and piping design
- Equipment selection and sizing
- Energy efficiency and environmental impact
Heat load calculations determine the amount of heat required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. System layout and piping design ensure that the heat is distributed evenly throughout the building. Equipment selection and sizing ensure that the system is properly sized to meet the heating demands of the building.
Energy efficiency and environmental impact are also important considerations. Hydronic heating systems can be designed to minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Installation and Maintenance
Installing a hydronic heating system involves several steps:
- Site preparation
- Component installation
- System testing and commissioning
Site preparation involves preparing the building for the installation of the heating system. Component installation involves installing the heat source, piping, tubing, radiators or radiant floor panels, and control system.
System testing and commissioning ensure that the system is operating properly and meets the design specifications.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of a hydronic heating system. Maintenance procedures include checking and cleaning the heat source, flushing the piping and tubing, and inspecting the control system.
Applications and Examples
Hydronic heating systems are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential homes
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial facilities
In residential homes, hydronic heating systems provide comfortable and efficient heat distribution. In commercial buildings, they are often used to heat large spaces, such as offices, retail stores, and warehouses.
In industrial facilities, hydronic heating systems can be used to provide process heat, such as for drying or curing.
Questions and Answers
What are the benefits of hydronic heating systems?
Hydronic heating systems offer several advantages, including energy efficiency, comfort, and versatility. They can be used with various heat sources, including boilers, heat pumps, and solar collectors, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly option.
What are the different types of hydronic heating systems?
Hydronic heating systems are classified based on their heat source: boiler-based systems, heat pump-based systems, and solar-based systems. Boiler-based systems use a boiler to heat water, while heat pump-based systems use a heat pump to extract heat from the air or ground.
Solar-based systems use solar collectors to harness the sun’s energy to heat water.
How do I choose the right hydronic heating system for my home?
Choosing the right hydronic heating system for your home depends on several factors, including the size of your home, the climate you live in, and your budget. It is recommended to consult with a qualified HVAC contractor to determine the best system for your specific needs.