Three tenths of a milligram, a seemingly minuscule quantity, holds immense significance in scientific fields and everyday life. This measurement plays a crucial role in determining drug dosages, analyzing chemical compositions, and ensuring accuracy in various industries.
From pharmaceuticals to analytical chemistry, the precise measurement of three tenths of a milligram is essential for ensuring safety, efficacy, and reliability.
Measurement and Significance

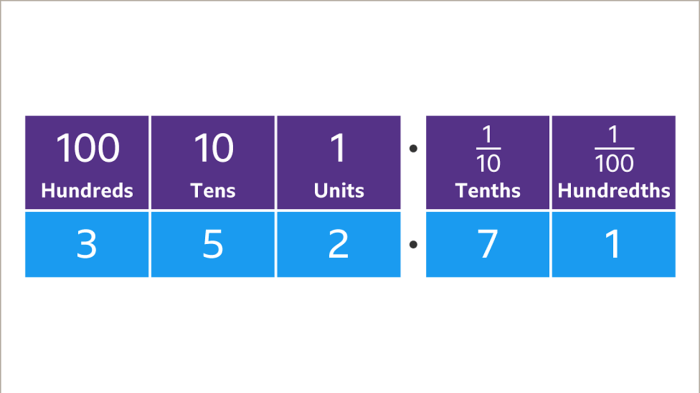
Three tenths of a milligram (0.3 mg) is a precise measurement of mass, commonly used in scientific and medical fields where accurate quantification is crucial.
In chemistry, it represents a specific amount of a substance, allowing for precise preparation of solutions, reagents, and samples for analysis. In pharmacology, it signifies a specific dosage of a drug, ensuring accurate administration and effective treatment.
Analytical Chemistry, Three tenths of a milligram
In analytical chemistry, 0.3 mg is often used as a reference point or standard for calibrating analytical instruments. This calibration ensures the accuracy and precision of measurements, enabling reliable analysis of samples.
Pharmacology and Drug Dosing

In the realm of pharmacology, the measurement of “three tenths of a milligram” plays a pivotal role in determining appropriate drug dosages. This precise measurement serves as a fundamental unit for calculating and administering safe and effective doses of medications.
To ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes, healthcare professionals rely on this measurement to accurately prescribe and dispense medications tailored to individual patient needs. By carefully calculating the appropriate dosage based on factors such as the patient’s weight, age, and medical condition, clinicians can minimize the risk of adverse effects and maximize the therapeutic benefits of the medication.
Calculating Drug Dosages
The measurement of “three tenths of a milligram” provides a standardized unit for expressing drug dosages. This allows for precise and consistent communication between healthcare professionals, ensuring that the correct amount of medication is administered to the patient.
The calculation of drug dosages involves several steps. First, the healthcare professional determines the appropriate dose per kilogram of body weight or body surface area. This value is then multiplied by the patient’s weight or body surface area to determine the total dose required.
Formula:
Dose (mg) = Dose per kg (mg/kg) × Weight (kg)
For example, if a medication has a dose of 1 mg/kg and the patient weighs 70 kg, the total dose would be 70 mg.
Administering Drug Dosages
Once the appropriate dosage has been calculated, it must be administered to the patient accurately. The measurement of “three tenths of a milligram” facilitates precise dispensing of medications, ensuring that the patient receives the exact amount prescribed.
Various methods can be used to administer medications, including oral tablets, intravenous injections, and topical creams. Each method has its own specific considerations and techniques to ensure accurate dosing.
Three tenths of a milligram is a tiny amount, but it can make a big difference in certain situations. For example, if you’re looking for a reliable and accurate way to assess your child’s language skills, you may want to consider using the PALS test version B . This standardized test is designed to measure a child’s receptive and expressive language abilities, and it can provide valuable information for parents and educators alike.
Three tenths of a milligram may seem like a small amount, but it can have a significant impact on your child’s future.
Analytical Chemistry and Instrumentation: Three Tenths Of A Milligram
Quantifying minute quantities like “three tenths of a milligram” demands meticulous analytical techniques and sophisticated instrumentation. These methods exploit various physical and chemical properties to determine the mass or concentration of a substance with high accuracy.
Spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry measures the absorption or emission of light by a substance. By analyzing the intensity of light at specific wavelengths, we can determine the concentration of a compound in a sample. This technique finds wide application in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and food analysis.
Chromatography
Chromatography separates compounds based on their physical or chemical properties. Techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC) are commonly used to identify and quantify compounds in complex mixtures. These methods have revolutionized fields such as drug development, forensic science, and environmental analysis.
Electrochemical Techniques
Electrochemical techniques utilize electrical signals to measure the concentration of ions or molecules in a sample. Methods like potentiometry and voltammetry provide valuable information about the redox properties and concentrations of substances. These techniques are crucial in industries such as electroplating, battery development, and environmental monitoring.
Precision and Accuracy in Measurement
Precision and accuracy are crucial when measuring “three tenths of a milligram.” Precision refers to the consistency of measurements, while accuracy reflects their closeness to the true value. Both are essential for reliable results.Factors affecting measurement reliability include instrument calibration, environmental conditions, and operator technique.
To minimize errors, it’s vital to use calibrated instruments, control environmental factors (e.g., temperature, humidity), and ensure proper operator training.
Calibration
Regular calibration of measuring instruments is essential to ensure their accuracy and precision. Calibration involves comparing the instrument’s readings to known standards and adjusting it as needed.
Environmental Factors
Temperature and humidity can affect the performance of measuring instruments. For instance, changes in temperature can cause instruments to drift, leading to inaccurate readings. Therefore, it’s important to control the environmental conditions during measurement.
Operator Technique
Operator technique can significantly impact measurement reliability. Proper training and adherence to standardized procedures can minimize errors. This includes following correct sample preparation, handling, and measurement techniques.
Conversion and Unit Analysis

Units of measurement play a crucial role in expressing quantities accurately. In pharmacology, it is essential to understand the conversion between different units of mass to ensure precise drug dosing. This section provides a comprehensive guide to converting “three tenths of a milligram” to other units of mass, highlighting the importance of using correct conversion factors.
Conversion Table
The following table presents the conversion factors for “three tenths of a milligram” to other units of mass:
| Unit | Conversion Factor | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Grams (g) | 0.0003 g | 0.0003 g |
| Micrograms (µg) | 300 µg | 300 µg |
| Nanograms (ng) | 300,000 ng | 300,000 ng |
Unit Conversion Accuracy
Accurate unit conversions are crucial in pharmacology. Using incorrect conversion factors can lead to errors in drug dosing, potentially affecting patient safety. Therefore, it is essential to pay close attention to the conversion factors and ensure they are applied correctly.
For instance, to convert three tenths of a milligram to grams, we multiply 0.3 mg by 0.001 g/mg, resulting in 0.0003 g. This precise conversion ensures that the correct drug dose is administered.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of three tenths of a milligram in pharmacology?
In pharmacology, three tenths of a milligram is a crucial measurement for determining appropriate drug dosages. It ensures that patients receive safe and effective doses of medication, maximizing therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
How is three tenths of a milligram measured accurately?
Analytical techniques such as gravimetric analysis, titrations, and chromatography are commonly used to measure three tenths of a milligram accurately. These methods involve precise instruments and standardized procedures to ensure reliable results.